Port 443 is used to secure communication travels between the client and the server.
Have you come here looking for answers to the queries you have about Port 443?
You have come to the right place.
This article will focus on HTTPS Port 443, how it works, what it protects, and why we need it.
Before that let’s talk a little about the port and how the port works.
What is Port?
There are different types of network ports numbered differently, like Port 22, Port 80, Port 443, Port 465 and so on. With these ports, a computer directs traffic to the correct places.
You may be aware that your system will reach out to the host server when you visit a website.
The process seeks out a connection on either the HTTP or HTTPS port, whichever is linked with web traffic.
After the server connects to the port, it sends back the website information, which your system will receive on the same port.
Ports see that the network connections make it to the right place. Also, they ensure that the traffic does not get messed up.
What is Port 443?
You must have visited the website that has HTTPS and a grey padlock in the browser’s address bar. It means a website connecting to the server over Port 443. The website has enabled an SSL certificate and it is secured. A normal website without SSL serves on Port 80. Port 443 indicates that the site is enough secured to carry online transactions without worrying about cyber theft. A website connecting to the server over Port 443.
You can now understand that Port 443 is a web browsing port used to secure web browser communication or HTTPS services.
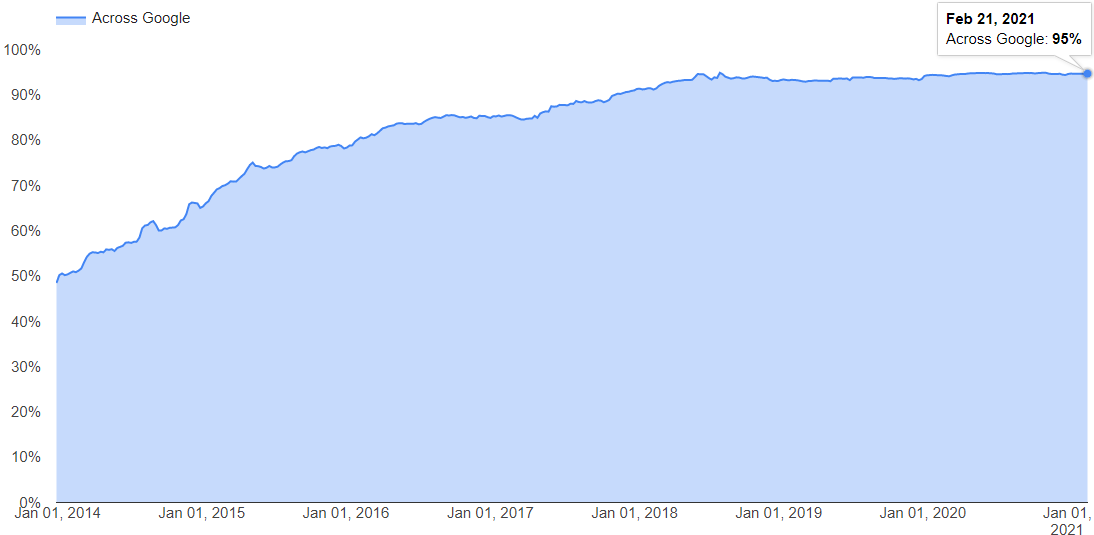
Over 95% of secured websites use HTTPS via port 443 for secure data transfer.
It will provide encryption and transport over secure ports. Thus, the data you transfer across such connections are highly resistant to third-party eavesdropping and interruption.
Moreover, the identity of the server that you connect remotely can be authenticated with confidence.
Once the connection is established, web browsers will display signs like a padlock, an unbroken key, etc. in the status region of your window, informing you about the secured connections.
Why is Port 443 chosen?
Currently, cyber thieves try to steal the information that travels between the server and the client. If the website does lack an SSL certificate means the site runs on HTTP instead of HTTPS, the information that passes in between two ends will remain in plain text. Port 443 assures that the website runs on a secured HTTPS version. However, if port 443 is not available, the site will load on the secured connection on Port 80. Thus, cyber thieves cannot intercept ongoing communication.
How to Enable Port 443?
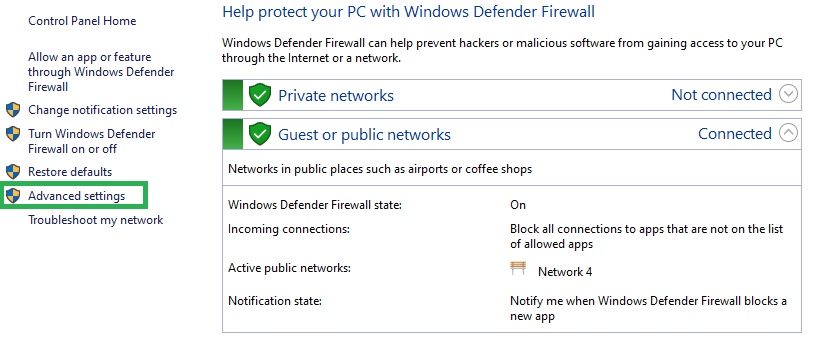
To enable Port 443, you need to add it to the Windows Firewall.
Step #1: Go to Firewall Control Panel by selecting start>>Run and type “firewall.cpl”.
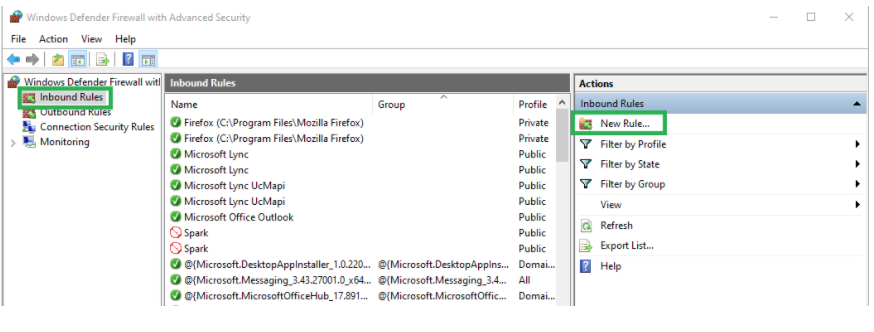
Step 2: On the left side, click on “Advanced Settings” then, click on “Inbound Rules” showing on left side.
Step 3: Now, click on “New Rule” on the right-side panel under the “Action” heading as shown in the above image.
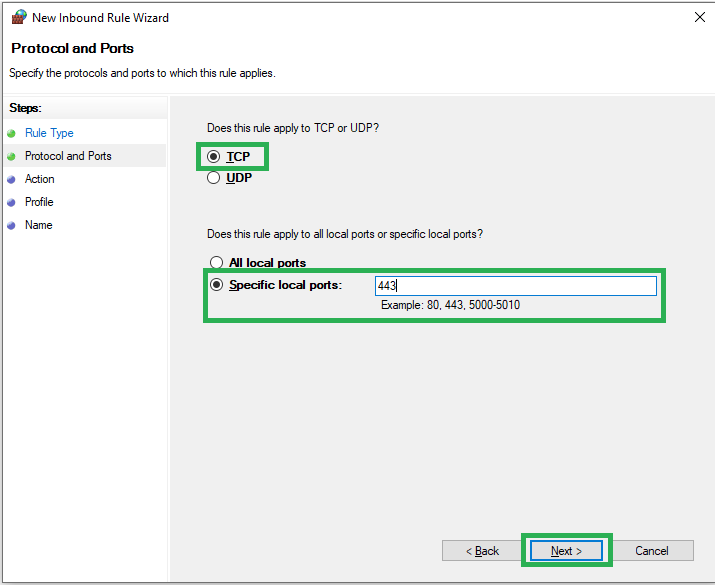
Step 4: You will have a new window where choose “Port” and click the “Next” button.
Step 5: Now, select “TCP” and “Specific local ports” where you need to write 443 in the given box.
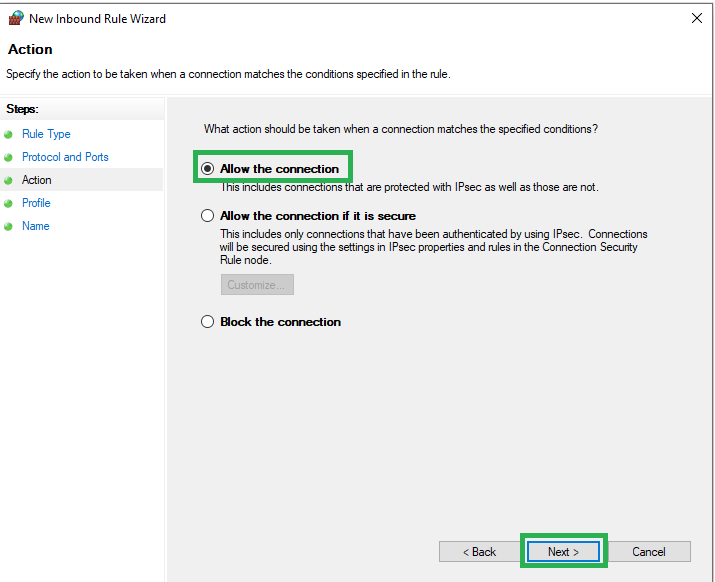
Step 6: In the next screen, “Allow the connection” and click the “Next” button.
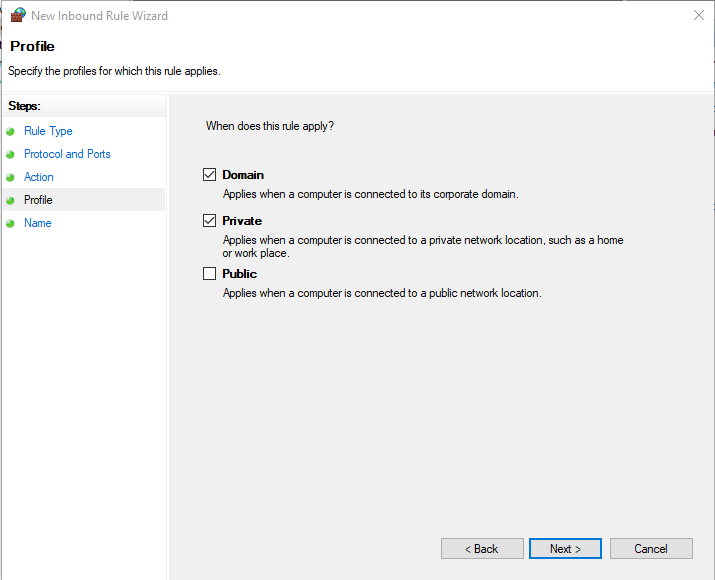
Step 7: Now, select the ‘Domain’ and ‘Private’ options and click the ‘Next’ button.
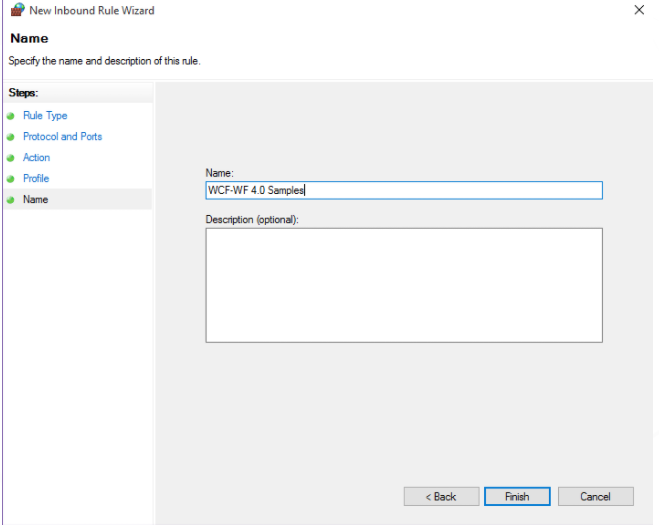
Step 8: Here, in the next window, type the ‘WCF-WF 4.0 Samples’ name and click on the ‘Finish’ button.
To continue with Outbound Rules, you need to follow steps# 2 to 8.
What does HTTPS Port 443 protect, and why do we need it?
HTTPS provides security to the data or sensitive information shared between your browser and the server. It ensures that your ISP (or anyone else on the network) cannot read or interfere with the conversation by encrypting the exchanges and granting privacy.
The SSL certificate features a lock icon that will appear on your address bar when you install it. It is an indication that your site is secure.
But do not be misguided about this secure lock feature. It sure does encrypt the communication channel, but it does not guarantee that an attacker will not regulate the website you are connecting with.
Moreover, if there are weak spots on your site, hackers will take advantage of them and compromise your data. Installing an SSL/TLS certificate is not enough to ensure that your website will never be attacked.
Note that while HTTPS will encrypt application layer data and secure it, the extra information added to the network or transport layer may be exposed.
When your browser makes an HTTPS connection, a TCP request is sent through port 443 to establish the connection. In the process, the data transferred between the client and the server is encrypted. But it cannot safeguard users against fingerprinting attacks.
The type of information that an attacker can access include:
- The user’s IP address and location
- Data size
- The linked website
- The number of times the connection is made
Now, coming to why HTTPS port 443 is important, if you are running a website that demands security such as banking, shopping, etc., you will be exchanging payment information on your site.
Encryption is crucial to protect sensitive information. With regular HTTP, all the information you exchange between your computer and a website will be readable by anyone as they will be available in plain text.
Moreover, your customers will be reluctant to deal with your business when you do not give online security importance and show authenticity. An HTTPS site can gain your customer’s trust.
There are other benefits associated with an HTTPS site, including ranking higher in search engines, updated browser levels, and increased conversions.
How does HTTPS work?
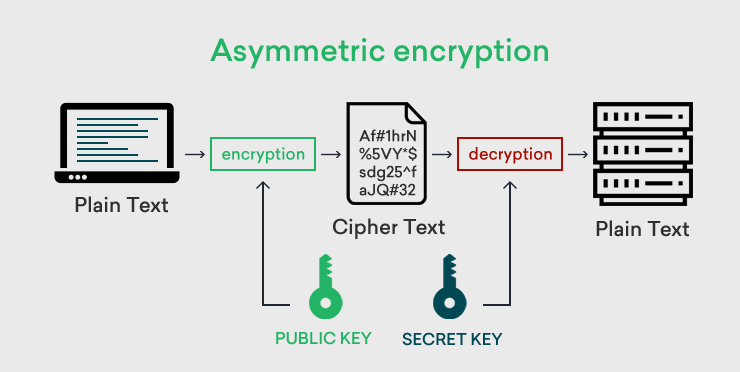
HTTPS makes use of an encryption protocol called Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt communications.
This protocol secures communications using the asymmetric public key infrastructure. This security system implements two different keys to encrypt communications between two parties, known as the private key and the public key.
The web owner has control over the private key, and it lives on a web server. Its function is to decrypt information that the public key encrypts.
The public key is available to all who want to interact with the server securely. When the public key encrypts information, only the web owner can decrypt it using the private key.
Whenever you browse an HTTPS site, and your browser connects to the server, the server responds with its certificate. This process is called the SSL handshake.
The goals are:
- To assure the client that it is connecting to the right server.
- For both the parties to have consent on a cipher suite. It includes which encryption algorithm will be used during the exchange of data.
- For both parties to have consent on any required keys for this algorithm
Source : Medium.com
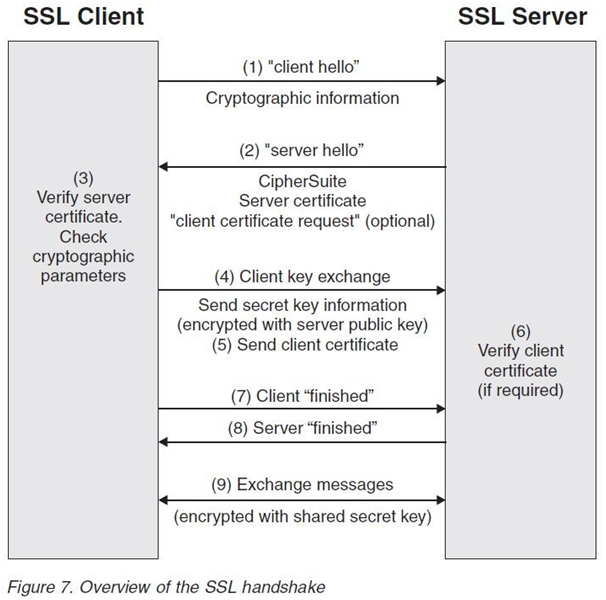
The main object of the SSL handshake is to provide data integrity and data privacy to the information passing between the client and the server. The SSL handshake process includes multiple steps that take place between the client and the server and all process is done in the background. The exact steps depend upon the key exchange algorithm and supported cipher suites.
Client Hello: A client starts the process with a “Hello” message to the server. It includes the cipher suits and TLS/SSL version, thread of random bytes (client random).
Server Hello: The server sends back a “Hello” message, with an SSL certificate, the selected cipher suits from the setlist by the client, and a string of random bytes (server random).
Authentication: The client then checks the identity of the server with the provided SSL certificate. It is to be checked with the available certificate authorities’ public key list.
Premaster Secret: Once the identity of the server and the SSL certificate authenticity is confirmed, the client sends an encrypted string of random bytes using the server’s public key. The public key is available with the SSL certificate. This string of random bytes can be decrypted with a private key of the server. This process of sending an encrypted string of random bytes is named Premaster Secret.
Decryption of Premaster Secret: The server receives the encrypted string of random bytes and decrypts it with its private key.
Session Key Generation: Now, both the client and the server create session keys using client random, server random, cipher suite, and premaster secret.
Client Finished Message: The client sends an encrypted Finished message with the session key.
Serve Finished Message: The server once receives the message from the client, sends its own encrypted finished message with the session key.
Secured Connection laid down: The SSL handshake process thus completes, and further encrypted messages will be exchanged using session keys.
Few Points to consider: In the SSL handshake process, it is noted that the SSL certificate should be active and not expired. The SSL certificate should be issued by a reputed certificate authority. The user should not face any SSL warning due to improper installation of the certificate. The installation error includes missing root or intermediate certificates or expired root and intermediate certificates.
HTTPS Everywhere: You can enable HTTPS Everywhere add-on from the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), which is available for Chrome, Safari, and Firefox. Else, you can go to the Extension section in Chrome browser and add it to the chrome browser.
Wrapping Up
Now that you are clear about HTTPS port 443, do you plan to switch your site to HTTPS? By doing so, you will enjoy improved security and all the other benefits mentioned in the article, including customer trust. If you implement SSL/TLS certificate and run your site over HTTPS port 443, it is a crucial step you can take to secure your site.