Authenticate server’s identity to the client as well verify client to the server with client certificate and server certificate.
When you visit a website, you may have noticed the “Not Secure” warning. This warning is shown by Google and other predominant browsers when you visit the sites that do not use SSL certificates. The websites having valid SSL certificates are marked as safe by almost all the search engines, which also gives a boost to their rankings on SERPs (Search Engine Result Pages).
An HTTP secured site has a padlock sign on the left of the browser. You can further confirm the validity of the SSL license by clicking on the padlock symbol.
In today’s world, online business/trade has become very popular among the online population because of the ease of buying and selling goods while sitting at your home. You do not need to travel outside for shopping; instead, you can use your bank accounts and debit/credit cards to make purchases online. But with this ease, there is also a threat of cyber-attacks to the online users that are continuously increasing.
Cyber-criminals use different tricks to steal the resources of websites or customer’s sensitive information like credit card details, usernames, passwords, etc. They then use this data to steal money from the target’s bank account or to perform any other malicious activities for their benefit. To keep you safe from these threats, client certificates and server certificates are used. These certificates make sure that the exchange of information between the browser and the website is encoded and is beyond the reach of hackers.
The adoption of client and server certificates is effective in protecting the communication between the two engaging parties. However, both are different from each other. Let us first discuss the purpose of both certificates before exploring the variations between the two.
What is Server Certificate?
A server certificate is commonly known as an SSL/TLS certificate that confirms the authenticity of the website. When installed on a server, a secure sockets layer (SSL) certificate changes the security protocol from HTTP to HTTPS. This leads to the web browser displaying indicators (like a padlock sign on the browser) to verify the validity of the site. This is done to assure the authenticity of the website to the clients.
Apart from this, SSL certificates also provide encryption for the data transmission between the server and the browser. This means that all the data transmission with this site is secured from any cyber-attacks that may emanate from someone listening on the communication channel with the intent of stealing the exchanged information.
What is Client Certificate?
A client certificate is, however, different from a server certificate. The client certificate is used to authenticate the validity of the user. The user might be a website visitor or an email user. To make it simpler, client certificates work as passwords but do not require any input from the client. Once the server validates the identity of the client certificate, a secure connection is established for data transmission.
The answer to “why client certificates are used instead of passwords” is the vulnerability of passwords. Passwords are just not enough to secure a system or validate a client as they can be cracked by brute-force attacks or any other password cracking techniques. That is why securing your sensitive information via passwords is risky and not full proof.
There might be some files or documents that you want to be accessed only by a few selected parties. As you know, passwords are not suitable for this work so you would look for other methods to perform this job. And that is where Client certificates step in. Client certificates validate the identity of the users by the system they use instead of verifying through user-provided passwords. If the client does not have authorized permissions, he/she would not be given access to the document or file. You can combine the use of passwords with client certificates to add another security layer. This will become a 2-step verification process, also termed as “two-factor authentication (2fa)”. Two-factor authentication makes your valuable documents more secure and is a must for organizations that deal with the sensitive data of their employees or customers.
Client certificates do not encrypt or decrypt any data, unlike server certificates that encode and decode the information shared between a user and a web server. However, one similarity between the two certificates is that both use public key infrastructure (PKI) for validation.
Client Certificate vs Server Certificate – the Difference
As you have now become familiar with the working of both these certificates, we can get down to comparing both of them for a better understanding of their variation.
A client certificate authenticates the client, and a server certificate validates the server – this is an evident difference that you can notice simply by the name. But there are some significant disparities in their working too.
The main differences between the server certificates and the client certificates are described below:
1. Identification
A server certificate is used to vouch for the authenticity of the server to the user. In contrast, a client certificate is used to confirm the validity of the client to the server.
2. Encryption or Decryption
Server certificates are used by the websites to ensure the confidentiality of the info shared between a user and a web server. These certificates encode the data coming from the user and decrypt it via the server’s private key. The server then sends back the response in encrypted form to the client to assure the privacy of the data.
However, client certificates do not perform encryption/decryption of data.
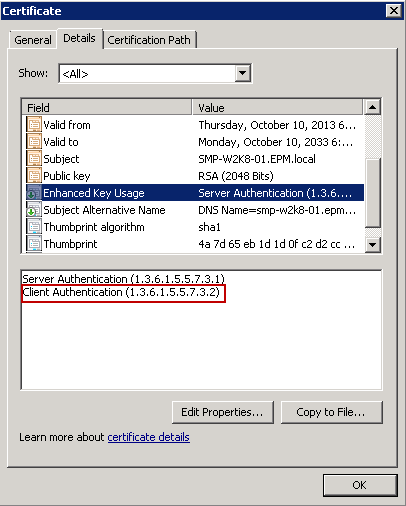
The object identifier (OID) for verification of the server certificate is 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1, and the OID for validation of the client certificate is 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2.
You can check this yourself too by clicking on the “View Certificate”. Then in the details tab, click on “enhanced key usage” to find the identification of your certificate.
An example of a client certificate is an email client certificate whereas SSL certificates are an example of server certificates.
The similarity between Server Certificates and Client Certificates
Both the certificates have two things common in them:
1. Both client and server certificates are based on public key infrastructure (PKI).
2. Both the certificates have “issued to” and “issued by” fields to carry the owner and the issuing authority’s identity, respectively.
Conclusion
Server and client certificates help secure both the communicating parties, i.e. the folks who are running an internet-based business and the ones using online shopping methods to make purchases through their ATM cards or bank accounts. In any case, you need to secure yourself from online risks and threats while transacting on the internet. For this, the clients must use a client certificate, and the website owners must install a server certificate for safe online transactions. These certificates protect your data from the reach of attackers – making online business secure for your safety.
Related Post: