Digital Certificate is a set of electronic credentials that are used to verify the certificate owner’s identity through encryption keys. These keys digitally encrypt and signs information. The certificate ensures that the certificate contains a public key that belongs to the SSL requestor to which the certificate was given.
What is Digital Certificate?
A digital certificate contains two keys a public key and a private key. A public key resides in a certificate while the private key is with the recipient. A message encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted with a private key.
When a certificate authority issues a certificate, it includes encryption algorithms, digital signature, serial number, expiry dates, and name of a certificate owner.
The certificate issuance process starts with submitting the CSR (certificate signing request) and submission of the required information. Once the information is submitted, domain ownership is verified along with business registration documents (if required). After verification, the certificate authority issues a digital certificate that needs to be installed on the server.
How Does Digital Certificate Works?
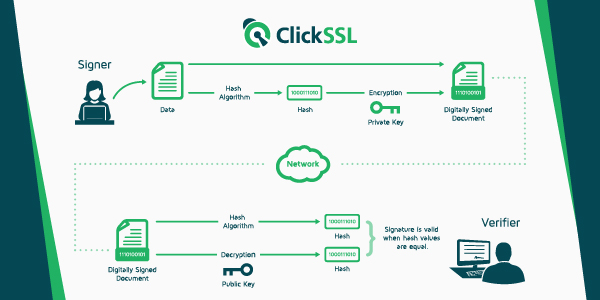
Like handwritten signatures, digital signatures are unique to every signer. Providers of digital certificates usually follow the Public Key Infrastructure protocol (PKI). In short, the workings of a digital certificate are based on the PKI protocol. With PKI, the provider applies a mathematical algorithm to generate a public key and private keys.
Upon the signer electronically signing a document, a signature will be created using the signer’s private key. The private key stays protected in the custody of the signer. The mathematical algorithm operates as a cipher that creates data that matches the one on the signed document. This data is referred to as a hash and can be said to be encrypted. Any alteration to the document will lead to the invalidation of the digital signature.
The figure below summarizes the working of a digital certificate.
To understand more, let us use the following example: Assume that Donald signs an agreement to sell a timeshare to Barack using a private key. Barack will receive the document together with a copy of Donald’s public key. In any case, the public key fails to decrypt the signature (from the cipher in which the keys were generated), it means the signature is not Donald’s, or it has been tampered with since it was signed. In that case, the signature will be considered invalid.
How are Digital Certificates Used?
The following are some of the ways in which a digital certificate can be used:
- Digital certificates are important in the security of debit card and credit card transactions. Debit cards and credit cards are usually embedded with digital certificates that ensure safe transactions with banks and merchant accounts.
- Computer hardware manufacturers apply digital certificate technology by embedding them into cable modems to safeguard broadband service from thefts and alterations.
- Digital payment companies vastly apply digital certificate technology in authenticating their ATMs, point-of-sale equipment, and kiosks.
- Websites use digital certificates (SSL certificates in particular) to secure browser-server communications and to show they are trustworthy and genuine.
- Email providers also employ digital certificate technology in securing emails to identify one user to another and for electronic document signing. Here, the email sender will electronically sign the mail while the receiver will verify the signature.
What Are the Benefits of Digital Certificate?
Digital certificates continue to play significant roles in the cybersecurity landscape. Some of the vital benefits of having a digital certificate include the following:
#1. Data Security, Confidentiality, and Integrity Through Encryption
One of the most important roles that digital certificates play is the safeguarding of sensitive data. Digital certificates prevent information from being seen by those not authorized to see the information. As a result, individuals and businesses carrying large troves of data will benefit from having a digital certificate. Take the example of an SSL certificate that helps encrypt data between website servers and website browsers and thus ensures that attackers cannot intercept data belonging to web visitors.
Digital certificates also help to solve privacy and message confidentiality problems. They allow communicating parties to interact privately over a public network. Moreover, digital certificates help maintain data integrity by ensuring that the data in transit is not tampered with, intentionally or unintentionally.
#2. Authenticity or Identification Benefits
In an age of widespread data breaches and surging cyberattacks, digital certificates have been on the frontline in the war against fraudsters and illegitimate websites masquerading as genuine ones. They identify all parties in the communication line and prove that websites and servers are really what they say they are. As you know, certificate authorities often research a business or website before issuing a digital certificate. All the relevant information about the website will be included in the certificate details. It is this information that helps to establish the authenticity of the website.
#3. Scalability
Digital certificates such as SSL certificates give the same encryption strengths to businesses of all shapes and sizes. In addition, the certificates can be issued, revoked, and renewed in seconds, meaning they are highly scalable.
#4. Reliability and Cost-effectiveness
The responsibility of issuing digital certificates lies in the hands of trusted certificate authorities. For the CA to issue one, it will need to rigorously vet an organization, meaning a hacker cannot trick organizations that use the certificates. Digital certificates continue to offer the required encryption strengths at a cost-effective price. It should not surprise you to learn that most digital certificates come at a price as cheap as $ 100 or less annually.
#5. Public Trust
Your website visitors are concerned about their security and would not risk visiting an insecure website. This is why most of them will want assurance that yours is a secure and genuine website. There are many ways you can use it to harness user trust, and one perfect way is to acquire a digital certificate.
Difference Between Digital Certificate and Digital Signature
A digital certificate is a set of electronic credentials (file or passwords) issued by a trusted certificate authority and attached to electronic messages/communications to prove the authenticity of the sender, device, or server, using the public key infrastructure (PKI).
On the other hand, a digital signature is a hashing model that uses the numeric string to provide authenticity and validate the identity of the users. In essence, a digital signature is fixed to an email or document using cryptographic key technology. When the receiver receives the message, the signature performs the same hash function to decrypt the message.
Read indeapth here : Digital Signature vs Digital Certificate
Types of Digital Certificates
#1. TLS/SSL certificate:
TLS/SSL certificate is installed on the server to encrypt the information that travels between the server and the browser. The server can be any type of server like LDAP server, web, app, or mail server on which authentication is needed for encrypting and decrypting the data. When a TLS certificate is on the website, the URL will start with HTTPS instead of plaintext HTTP. TLS certificates can be of different types like single domain, multi-domain, wildcard SSL, and multi-domain wildcard SSL.
Single Domain SSL: Single domain SSL only secures a single domain/subdomain with strong encryption. It is available at an affordable price and can be ideal for blogs, forums, and single domain websites. This certificate covers www and non-www versions, for example, www.domain.com and domain.com.
Multi Domain SSL: Multi domain SSL aka SAN SSL certificate can secure multiple domains and subdomains at a very nominal price and this certificate can be installed on multiple servers. The certificate has the ability to safeguard up to 250 domains (depending on the provider). Below is an example of a multi-domain SSL certificate.
- www.domain1.com
- blog.domain.com
- mail.domain2.com
- payment.subdomain1.domain2.com
Wildcard SSL: Wildcard SSL certificate is ideally for the protection of the first level of subdomains related to a primary domain. All subdomains will have the same level of encryption (SHA-2) as per the CAB/forum standards. You can add an unlimited number of subdomains to the wildcard SSL certificate without spending any extra penny. You can check the below example of wildcard SSL.
- *.domain2.com (Primary domain)
- blog.domain2.com (subdomain)
- mail.domain2.com (subdomain)
- payment.domain2.com (subdomain)
- autodiscover.domain2.com (subdomain)
Multi Domain Wildcard SSL: Multi-domain wildcard certificate is an ideal way to secure different levels of wildcard domains and subdomains, which are needed to be secure with robust encryption. A single wildcard SSL can secure one primary domain and subdomains but a multi-domain wildcard can secure different wildcard domains and their subdomains. The below example can clarify multi-domain wildcard SSL certificates where a different level of domains can secure their subdomains.
- *.domain1.com
- *.subdomain1.domain2.com
- *.a1.subdomain2.domain3.com
- *.a2.subdomain.mydomain.com
#2. Code Signing Certificate:
Code Signing certificate authenticates the publisher’s identity and ensures code integrity. Code signing certificate follows two types of validations like organization validation and extended validation (EV Code Signing certificate). If we talk about the EV Code Signing certificate, then EV Code signing with the help of the Microsoft Smart Screen filter builds the reputation of the publisher. Generally, the developer uses a private key to sign a code and users apply a public key to verify the publisher’s identity. Few famous brands deal with Code Signing certificates.
Comodo Code Sign: Comodo Code Signing certificate is a branded certificate that authenticates the code and assures users that the code is from the original source. Moreover, a timestamp will never let your code invalid even if the certificate itself expires. It helps to increase downloads of software and assures that the code is not modified since it is signed.
Comodo EV Code Sign: Comodo EV Code Signing certificate builds immediate publisher’s reputation with Microsoft SmartScreen filter technology. Distributors can distribute software code easily on third-party platforms also. Comodo thoroughly checks business existence with third-party sources too. Comodo EV Code Sign certificate removes pesky download warnings. A private key is kept on an external hardware token to avoid hacking activities.
DigiCert Code Signing Certificate: DigiCert Code Signing certificate can sign code for drivers, software, applications. The certificate confirms that the code is from the original source and not tampered with. Due to organization validation, DigiCert checks business presence with registered business documents and third-party databases. Users will not get an ‘Unknown Publisher’ warning while downloading the software. The code signing certificate supports multiple platforms (Java, Adobe AIR, Office, and VBA, MS Authenticode, Windows phone).
#3. Client Certificate:
A client certificate is a data file that authenticates the client’s identity to the server. There is no data transmission involved in the client certificate. A client certificate is also named an email certificate in which the email sender signs the communication, and the receiver confirms the digital signature. In the browser, the Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) is represented as client certificate OID (object identifier) under Extended Key Usage details. When a user requests to access a secured database, it has to pass through two-factor authentication in the client certificate.
Who Can Issue a Digital Certificate?
Certificate authorities are the ones tasked with the issuance of digital certificates. They will sign the certificates to prove the validity and authenticity of the organization that requested the certificate. The certificate authority is primarily responsible for managing the verification of domain control. Essentially, certificate authorities play a crucial role in the public key infrastructure process and secure the internet.
Conclusion:
Each certificate has its importance and is useful in different situations like the TLS certificate is for securing online transactions where the Code signing certificate is to sign software code. However, the object of a digital certificate is to verify the identity and encrypt the information. A digital certificate is necessary to provide integrity, authenticity, and Non-repudiation and all these elements are required in the security world.