Most website owners purchase SSL certificates and install them on their websites to encrypt sensitive information and protect it from hackers. It forced them to buy dedicated IP addresses for each domain name, which proved to be expensive and hard to manage.
Things changed when Server Name Indication came, and it provided the owners with the chance to own multiple domains on the server using one SSL certificate. SNI reduced costs and made it easier to manage several domains without too much struggle. The guide will explain how server name indication works and why you should consider using it, especially when dealing with multiple domains.
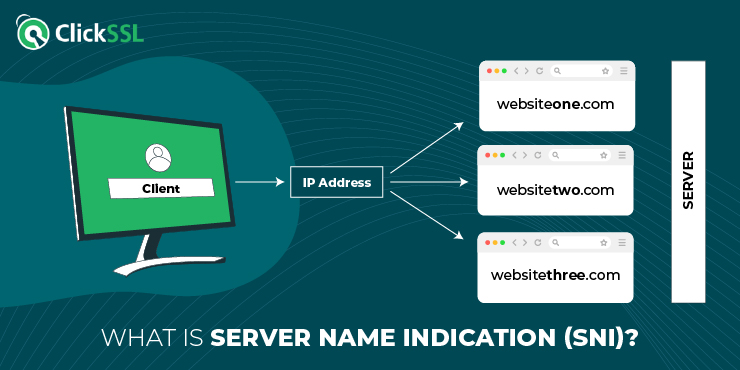
What is Server Name Indication?
It is an extension integrated into TLS protocols, enabling clients such as web browsers to specify the hostname they intend to connect to as part of the TLS handshake process. Since the TLS handshake normally occurs before the client’s device shows which site it would like to visit.
SNI allows several websites covered by HTTPS to get served using the same IP address using different certificates. It ensures that the proxy directs the client’s traffic to the right server.
Why Use Server Name Indication?
There are several benefits that one gets from using server name indication. The common ones are as follows.
- SNI improves efficiency by allowing servers to host multiple domains using a single domain. It makes the server more efficient and uses fewer IP addresses on many domains.
- SNI reduces any complexity that comes with managing several SSL certificates on several servers. It makes the management easier for all the IT professionals.
- SNI supports virtual hosting, where one server hosts several domains that share resources like memory, CPU, processors, etc. It makes it easier for system administrators and other IT professionals to manage many websites using fewer servers. SNI also makes companies lower costs of operation as they will be using fewer servers that cost less.
- Server Name Indication utilizes resources properly by hosting multiple domains on a single server so you can use your resources properly without wasting some of them.
How Does Server Name Indication Work?
Server Name Indication establishes connections between the server and the client when someone visits a website. The server gets the message from the client, which is the browser, and it includes the hostname. The TLS handshake process starts when a client sends a message to the server. The message will consist of the server hostname it wants to connect to, a nonce, and a signal to show SNI compatibility with the server.
The server responds with a message consisting of a TLS version, a nonce, and the requested hostname SSL certificate. You will get an error message if the client doesn’t support SNI, and the whole connection will fail.
Whenever any client sends a request to the server, the HTTP Host header will carry the requested hostname, and the server will use it to decide which host to work with. The server and client finish the TLS handshake process if the server has a valid SSL certificate for the said hostname.
Features of Server Name Indication (SNI)
Here are some of the features of Server Name Indication. They are as follows:
- Better compatibility. Server name indication supports most servers and browsers, making it commonly used by many website owners.
- Good performance. SNI optimizes resources, i.e., processors, storage, etc., making it handle many requests, making users have a better user experience.
- Robust security. SNI leverages TLS and SSL protocols to protect websites from common cyber threats like man-in-the-middle attacks, cross-scripting, etc.
- Supporting multiple certificates. Website owners can install multiple SSL certificates on a single server, making it support multiple domains using one IP address.
- Cost reduction. Being able to host several websites on a single server makes it cheaper to get the addresses and host multiple websites on one server.
- Greater flexibility. SNI flexibility enables users to host several websites on one server, each with its SSL certificate, making management easier.
Differences between SNI and SANs
Despite the fact that SNI and SAN both host multiple websites on a single server, there are several differences between the two. The main difference is how they work. SNI helps servers host multiple domains and SSL certificates using one IP address, while SAN works with an SSL certificate to help website owners get one multi-domain SSL certificate that supports several domains and install it once.
SNI enables the server to choose which certificate will be in use based on the domain name provided by the client. SAN has Subject Alternative Names that you must also protect using your SSL certificate.
Disadvantages of Using SNI
Apart from having advantages, using SNI to host your websites has some disadvantages. Some of its shortcomings include:
- It only works with HTTPS protocol, making it hard for other protocols like SMTP and FTP.
- If you host multiple domains using one IP address and there is one with the address, all the multiple domains on your address get affected.
- When using SNI for SSL support, you can experience a lot of issues during the setup process, which might lead to management issues.
- In the event of an excessive volume of communication overload between the server and client, it can disrupt regular performance and lead to increased latency.
- While transmitting its data in plain text during the TLS handshake, SNI may expose sensitive information to hackers and malicious actors. Although there is an encrypted version of SNI, it doesn’t offer a guarantee of security.
What browsers support SNI?
Here is a quick list of the supported browsers:
- Mozilla Firefox version 2.0 and later.
- Opera browser version 8.0 and later.
- Safari version 2.1 and later.
- Google Chrome version 6.0 and later.
- Internet Explorer version 7.0 and later.
- Honeycomb browser version 3.0 and later.
Conclusion for Server Name Indication
There are instances where users may encounter errors when attempting to access specific websites, such as the “your connection is not private” error, which often signifies an issue with SNI. SNI, with its compatibility with most servers and browsers, remains a reliable choice to ensure the safety of your website for visitors. It tends to be more cost-effective and adaptable compared to traditional SSL certificates. This guide has provided a deeper understanding of SNI and its role in facilitating secured communication between clients and browsers.
Also Read: